Price
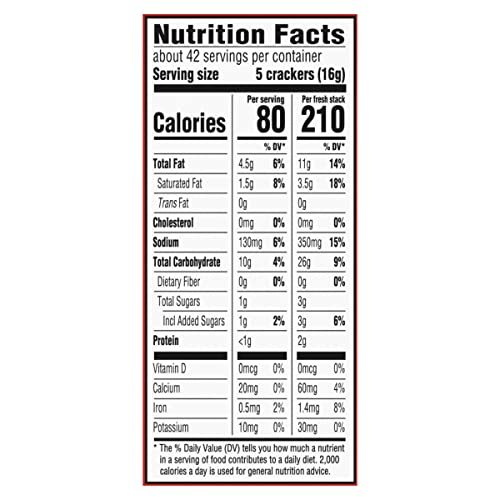
Premium DUX Crackers (Pack of 3)
The Chinese philosopher Confucius is known for his teachings on ethics, morality, and social harmony. His ideas have had a profound impact on the cultural, political, and social fabric of East Asian countries for over two millennia. Confucianism emphasizes the importance of social relationships, hierarchical order, and adherence to traditional rituals and practices.
At the heart of Confuciian philosophy is the concept of ren, which can be translated as "benevolence," "humaneness," or "love for others." Ren is the fundamental virtue that Confucius believed should guide all human interactions and relationships. Confucius taught that individuals should cultivate ren within themselves and extend it to their family, community, and society at large.
Another key aspect of Confucianism is the emphasis on filial piety, or the respect and obedience owed to one's parents and elders. Confucius believed that this form of loyalty and devotion was essential for maintaining social order and harmony. He also emphasized the importance of ritual and propriety (li) in regulating human behavior and fostering social cohesion.
Confucius lived during a time of political turmoil and social upheaval in ancient China. He sought to provide a moral and ethical framework that could help restore stability and order to a fractured society. His teachings on virtuous leadership, education, and the cultivation of the self became highly influential in the centuries that followed.
The Analects, a compilation of Confucius' teachings and dialogues with his disciples, is considered the foundational text of Confucianism. In this work, Confucius outlines his vision for a harmonious society, emphasizing the importance of moral cultivation, filial piety, and the proper fulfillment of one's social and familial roles.
Despite its enduring influence, Confucianism has also been the subject of criticism and reinterpretation over the centuries. Some have argued that Confucian ideals can be used to justify social inequality, authoritarianism, and the oppression of women. Others have sought to reframe Confucianism in a more egalitarian and humanistic light, emphasizing its emphasis on self-improvement, ethical behavior, and the cultivation of a harmonious society.
In modern times, Confucian ideas have continued to shape the cultural and political landscape of East Asia. The principles of Confucianism can be seen in the emphasis on education, social harmony, and respect for authority in many East Asian societies. At the same time, Confucianism has also been adapted and reinterpreted to address the challenges of the modern world, such as the need for greater individual rights, economic development, and environmental sustainability.
Overall, Confucianism remains a significant and enduring philosophical and cultural tradition that has profoundly influenced the course of East Asian history and continues to shape the worldviews and values of millions of people around the globe.
product information:
| Attribute | Value |
|---|